

The top of the hierarchy is called the root zone, and under it are zones for each of the top-level domains (TLDs). DNS is responsible for translating the human-readable domain name into the IP address.ĭNS is a hierarchical system. Whenever you visit a website, your computer needs to know the IP address of the website’s server so that it can connect to it.
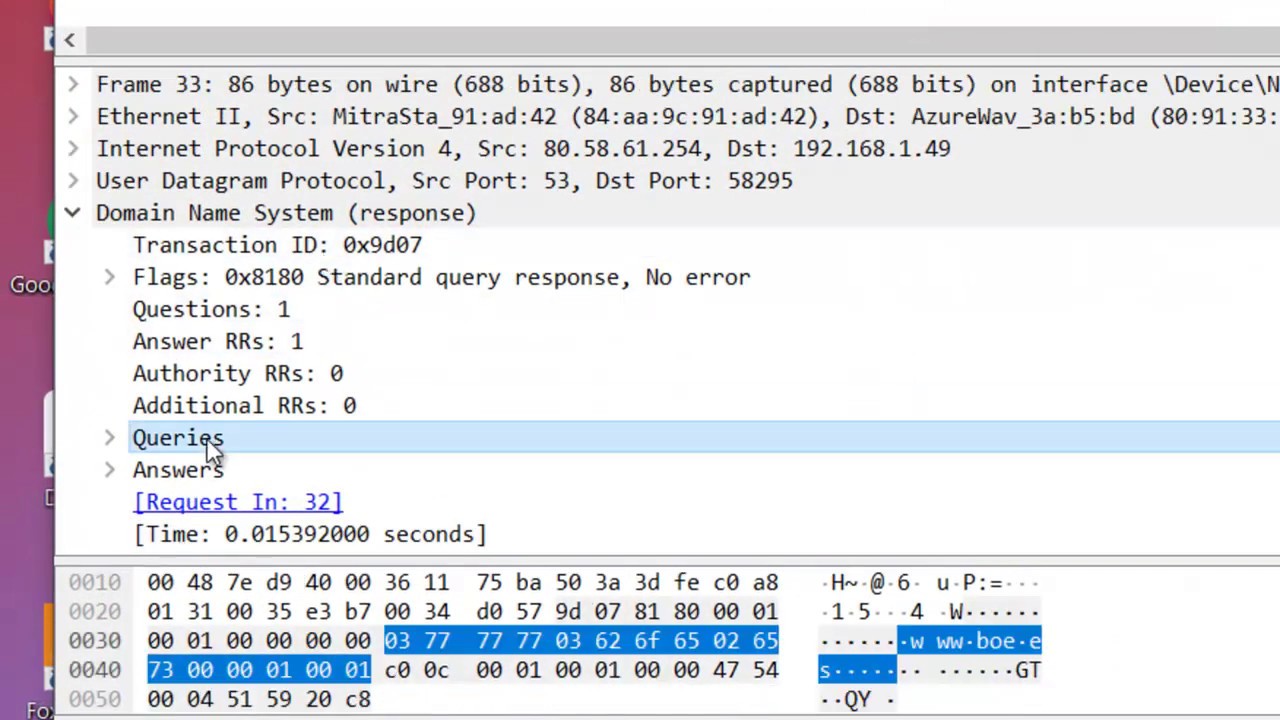
This process can take some time if there is not an exact match for the domain name in one of the DNS servers’ cache. The DNS servers query other DNS servers until they eventually find the IP address for the domain. Whenever you type a domain name into your web browser, your computer queries DNS servers to find out the IP address for that domain. It is simply a database that links meaningful names (known as host names), such as, to a specific IP address, such as 185.230.63.171. How to use tcpdump to filter DNS Query packets?ĭNS is short for Domain Name System.Capture DNS zone transfer Packets with Tcpdump.We can use tcpdump to filter DNS query traffic and DNS zone transfer packets to learn more about how DNS works. DNS is a basic part of the Linux admin task. Tcpdump is a very powerful Linux command to capture DNS packets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
